Refraction through prism
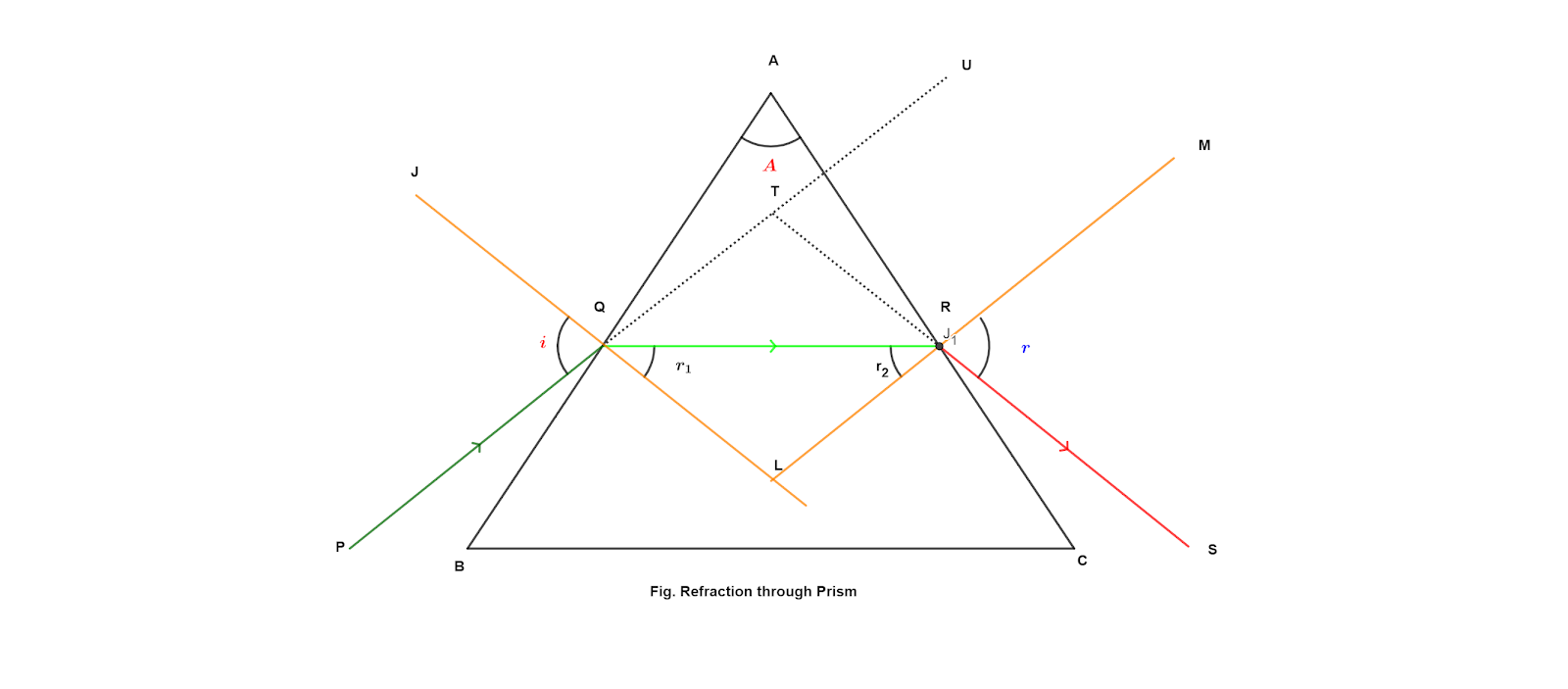
Consider a prism placed in air and a ray PQ be inicident on a refracting surface AB. The ray is then refracted along QR. The angle of incidence and angle or refraction are 'i' and 'r1' here respectively. The ray QR is then incident upon AC. Here, the light goes from optically denser medium to an optically rarer medium. If the angle of incidence in the denser medium 'r2' is not greater than the critical angle, the ray is refracted (emerge out) in air along RS. The angle 'e' is the angle of emergence. If the prism were not present, the incident ray would have passed undeviated along PQTU. Because of the prism, the final ray goes along RS. The angle UTS=δ is called the angle of deviation.
When the angle of incidence 'i' is increased from 00 , the angle of deviation first decreases, becomes minimum and then increases. The angle of deviation which is minimum at a particular value of angle of incidence is called the angle of minimum deviation . In this situation, i=e.
The relation between refractive index and the angle of minimum deviation is,
For a small angled-prism , δ=A(μ-1)
Grazing incidence and Grazing emergence
When a ray of light is incident on a face of prism (AB) with an angle of incidence 90°, the ray lies on the surface and is refracted through the prism. This refraction of the prism is called the grazing incidence . In this case, i=90° and r1=critical angle, c. When a ray of light is incident on face (AC) with an angle of incidence r2>c, then the angle of emergence e=90°. This refraction is called the grazing emergence.Click the link Prism to find the important questions on this chapter.


Comments
Post a Comment